Mapbender Quickstart: First steps with Mapbender¶
Mapbender is a web based geoportal framework to publish, register, view, navigate, monitor and grant secure access to spatial data infrastructure services. Management interfaces empower administrators who need to maintain and categorize map and feature services and grant access to individuals, groups and other services. Mapbender is written from the ground up using modern web technologies. The foundation is laid by Symfony. On the client-side expect to find OpenLayers.
With this code base, we will continue the Mapbender idea of being a Geoportal framework. Key features of Mapbender are:
Applications can be setup, configured and styled right from within the browser.
Services (e.g. WMS) can be managed inside a service repository and linked to applications.
Rights management are easy to maintain, for individual users and groups, whether you store them inside the database or in an LDAP.
Search modules can be configured.
Applications for digitalization can be setup.
Mobile template can be used to provide applications for smartphones and tablets.
You will need nothing but a web browser for this quickstart.
This quickstart describes how to:
Start Mapbender
Create an application
Insert elementes into an individual application
Configure sources
Manage users and groups
Use the rights management
Start an application at a defined position
This is how a Mapbender application can look like:
Installation¶
This quickstart explains the basics of Mapbender and serves as a quick introduction after your first successful installation. For the installation of Mapbender have a look at Installation.
1. Start Mapbender¶
Choose
Mapbenderfrom the start menu (if a shortcut was already created) or visit http://localhost/mapbender/app.php (this address can be slightly different depending on how the Apache Alias was created in the file /etc/apache2/sites-available/mapbender.conf, more information at Installation).The application should then appear in your browser window.
If you have any difficulties running Mapbender, please check whether your Apache web server and your PostgreSQL database are running without errors.
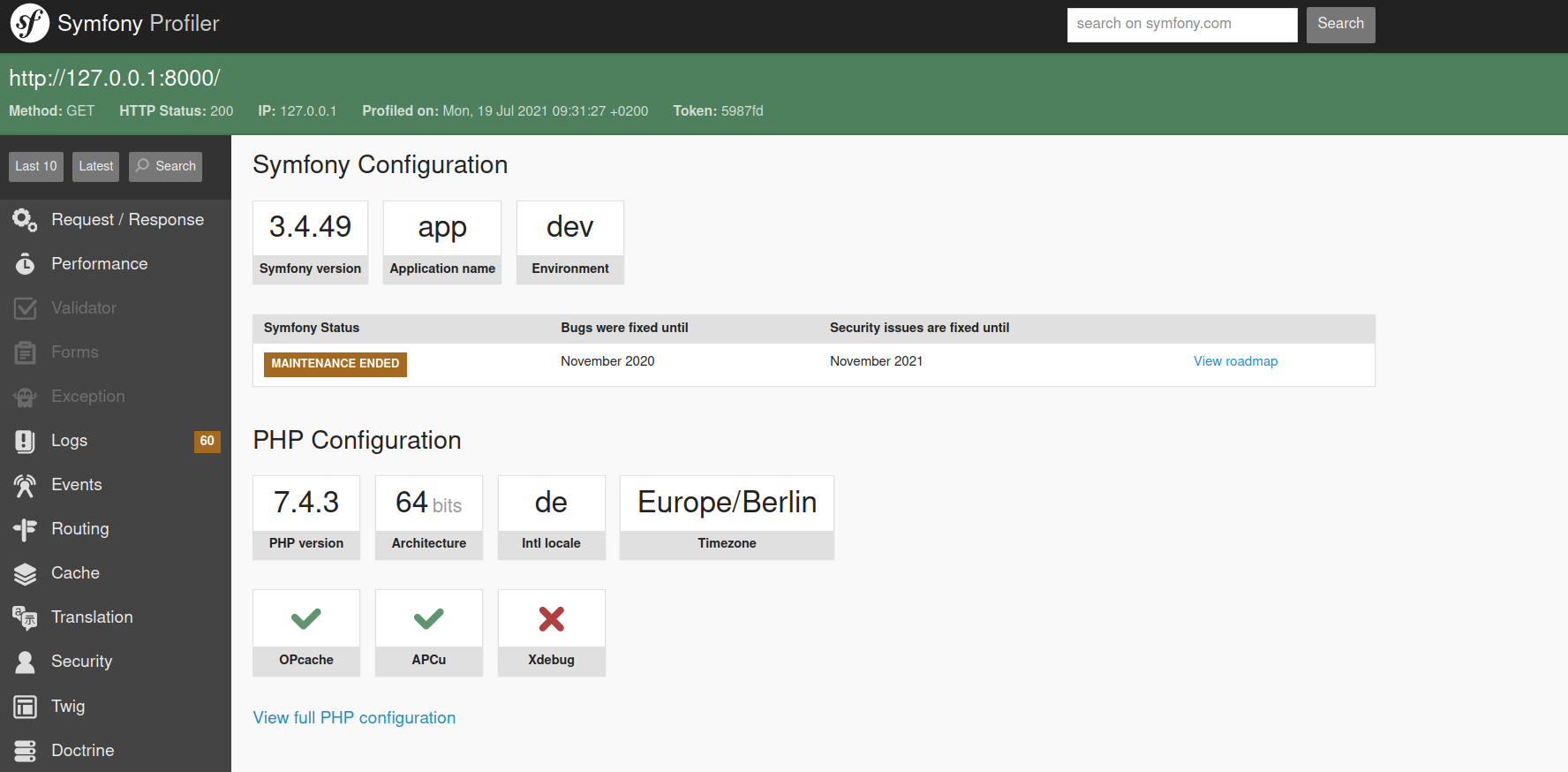
Start Mapbender in developer mode¶
Symfony offers a developer mode with lots of information about your application (logging, exceptions, database queries, memory usage, time and more). This mode is only available from localhost.
Start the developer mode: http://localhost/mapbender/app_dev.php
Have a look at the information that is offered in the developer mode.
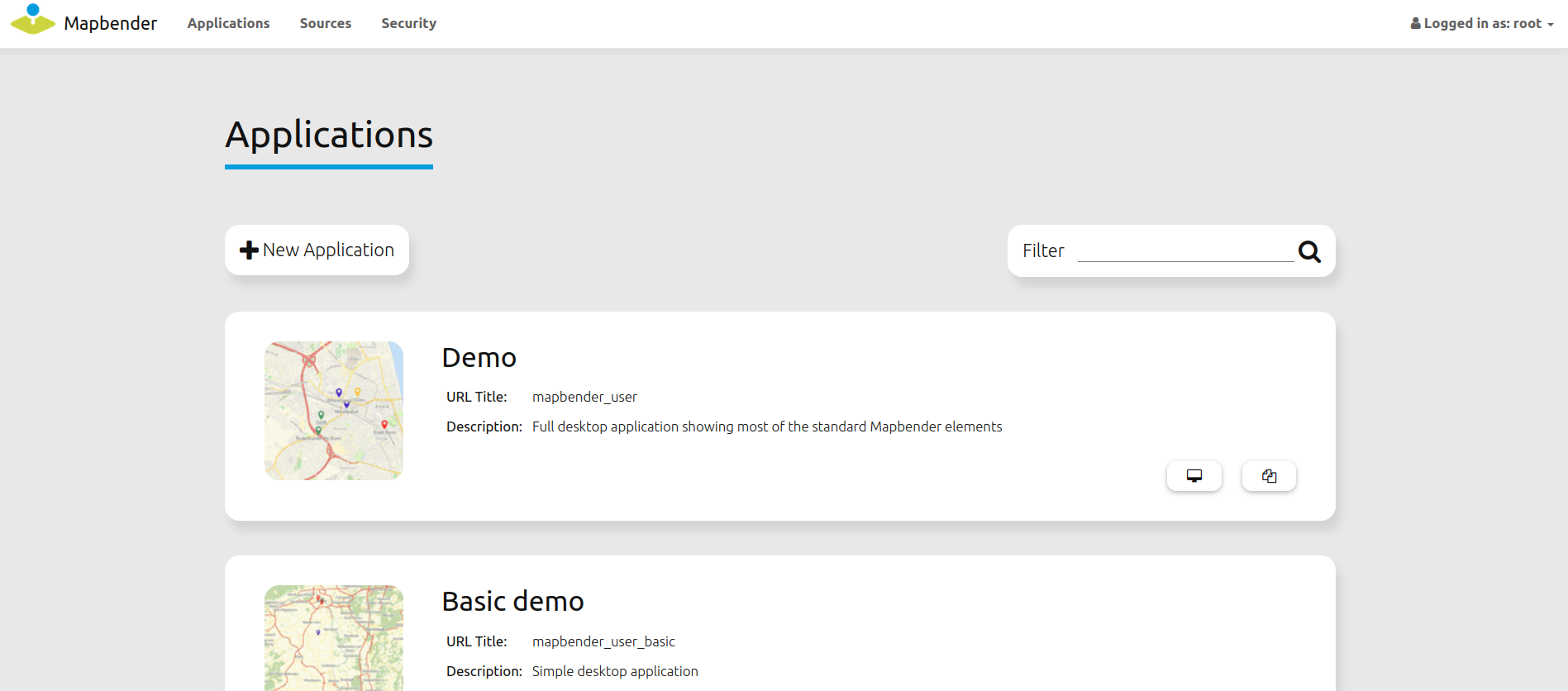
Mapbender Backend¶
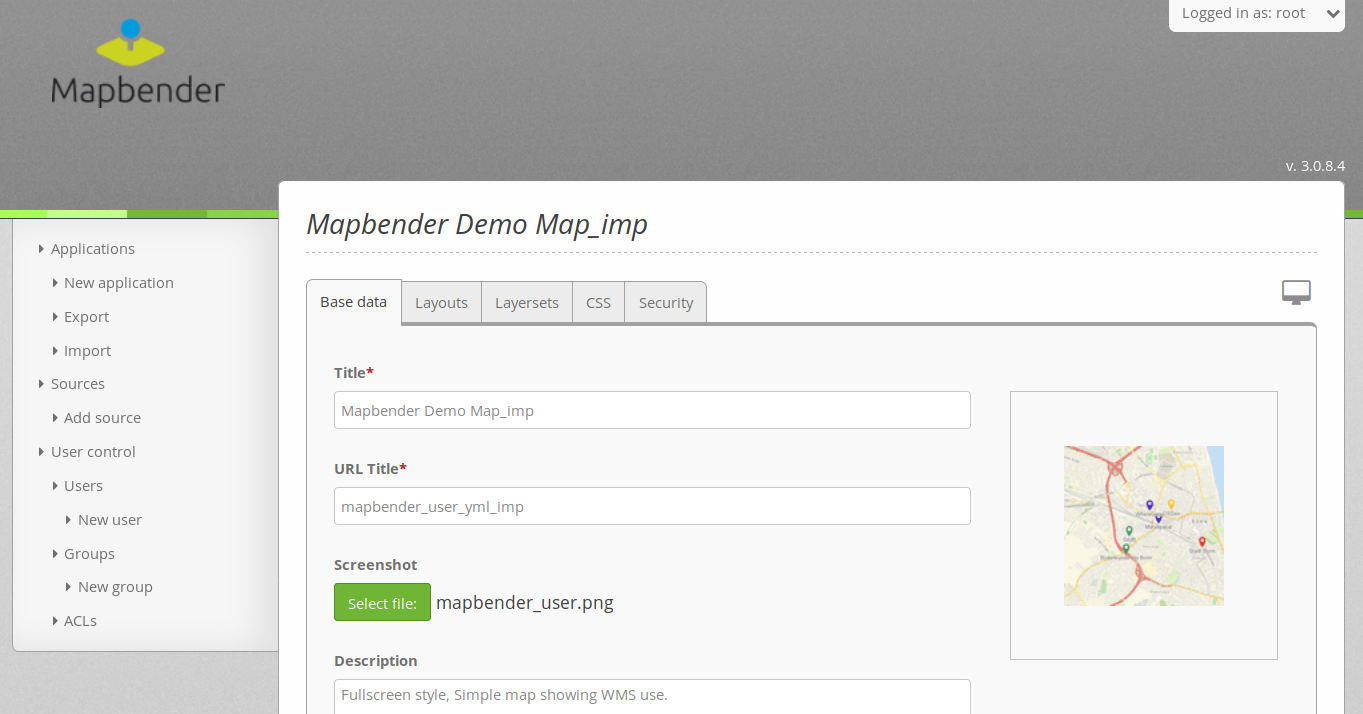
After a successful Mapbender startup, the application overview page in the backend will appear. The applications are listed with a screenshot, title, URL title and description.
You can open an application by click on the title, the screenshot or via the

button.A log-in is required to gain access into Mapbender’s administration backend. In order to do so, click on login at the top-right of the login page. You can login with the user that was generated during installation. This could be
rootwith the passwordroot- this is the default user and password that you get after installation of Mapbender. Please change the root password if you want to run a productive environment. Please don’t delete the user root.
After a successful login you will be directed to the Mapbender administration backend.
Application overview¶
The application overview site displays a list of all available applications. The root user has access to the following functions:
title, URL title and description
preview screenshot for the application (if provided)
filter textfield for application search
option to create new applications
link to the application
button to duplicate the application
button to export the application
button to edit the application
button to publish/unpublish the application
button to delete the application
2. Create an individual application¶
There are three different options to create an application:
An application can be created out of an already existing one. This can be done via a click on the  button in the application overview. The application will receive the same title and URL title with the appendix “imp”. All previously defined elements and configurations will be transferred as well. Another possibility is the import of an application. Further information can be found on the following page: yaml_de:yaml-application-files.
button in the application overview. The application will receive the same title and URL title with the appendix “imp”. All previously defined elements and configurations will be transferred as well. Another possibility is the import of an application. Further information can be found on the following page: yaml_de:yaml-application-files.
Furthermore, new applications can be created from scratch. The required steps are explained in the following:
Select the option “New Application” in the application overview.
After that, select a template in order to define the layout of your application. The options are: Fullscreen, Fullscreen alternative, Mapbender Mobile template. It is also possible to define your own template and assign it to a new application.
Tip
Please note that the style-, icon- and layout-configurations are set up via css- and twig-files. Read more about template generation at How to create your own Template?.
Define a title, URL title and a description (optional). Title and URL title can be identical. However, the URL title has to follow the usual URL syntax.
A thumbnail can be uploaded as well. It will appear next to the application title on the application overview page. For this, select “Select File” below the thumbnail section.
Under the section Map engine, choose your preferred OpenLayers version to manage the application’s map.
Set a tick at “persistent map state”, to make certain map parameters and configurations persistent. Further information can be found on the following site: share.
Click “save” to save and create your application. It is now possible to add elements (e.g. map, navigation bar, legend) and services to your applicaiton.
Applications can be re-edited at any point. In order to do so, navigate to the application overview. Here, you can click on a 
Button for every application with corresponding editing rights. Furthermore, applications can be viewed in the Frontend via a  Button. They can also be exported (
Button. They can also be exported ( ), deleted (
), deleted ( ) or made visible/invisible to not logged-in users (
) or made visible/invisible to not logged-in users ( ).
).
3. Add elements to your application¶
Mapbender consists of a toolbar, sidepane, content and footer. A variety of different elements can be added into these areas.
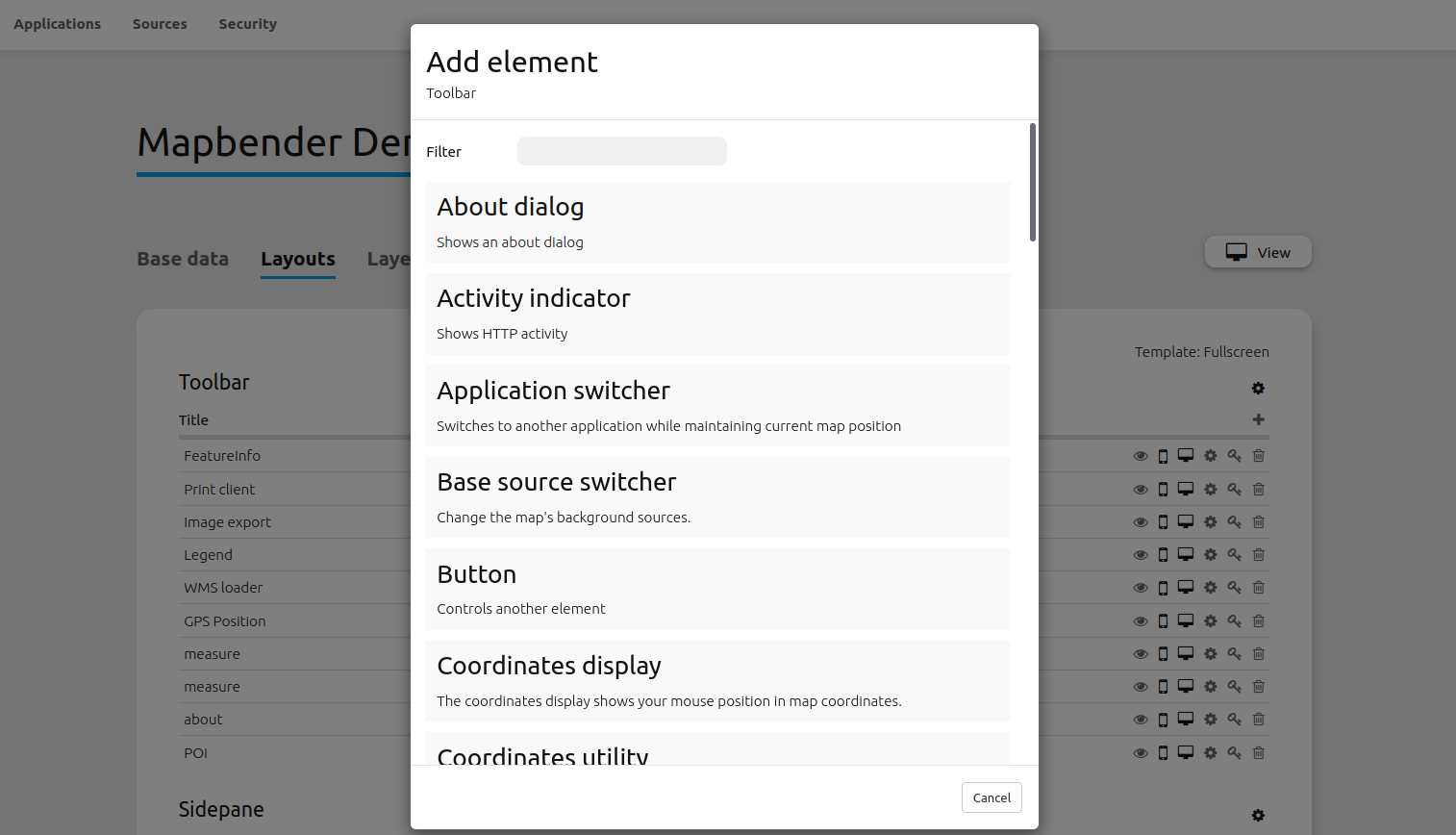
Choose
Applications -->
Button --> Layouts.Click on the

Buttonto get an overview over the elements Mapbender provides in the corresponding area.Choose an element from the list. Notice that you have different areas in your application. Make sure to add the element to a region that makes sense. Elements can not be added to all regions. For instance, the overview map is not integrable into the content.
Configure the element. Notice: When you select an element, for example map, you see that the element has a set of attributes. Each element offers individual attributes for configuration.
You can change the position of an element via drag & drop within and between regions.
Have a look at your application. To open your application, click on the

Button.
Now you should have an idea about how easy it is to change a Mapbender application.
In the following, you find a complete list of all elements and their functionalities. For a more detailed description, please have a look at the corresponding chapters in the mapbender documentation.
About dialog: Shows information about Mapbender in an about dialog
Activity indicator: Shows HTTP activity
Application switcher: Switches to another application while maintaining the current map position
Base source switcher: Changes the map’s background sources
Button: Integrate another element as a button
Coordinates display: Shows the map coordinates of your mouse position
Coordinates utility: Transforms coordinates to different SRS and navigates to them on the map
Copyright: Shows terms of use
Data manager: Create and manage non-spatial data
Digitizer: Create and manage spatial data
Dimensions handler: Manage sources with a time dimension
FeatureInfo: Gives information about sources
GPS Position: Renders a button to show the GPS position
HTML: Offers free definition of HTML to integrate pictures, texts or links
Image export: Exports the current map view (format options: png or jpeg)
Layer tree: Gives an overview of map layersets and layers
Legend: Displays legend of active themes on the map
Line/Area Ruler: Enables to measure a line/area and display its length/area in a dialog
Link: Links to an external URL
Map: Creates the map element in which layersets and layers are integrated into
Navigation toolbar: Provides a floating control to pan and zoom in the map
Overview: Provides an overview map (only available in Content section)
POI: Creates a POI for sharing
Print client: Renders a Print dialog
SRS selector: Changes the map’s spatial reference system
Scale bar: Displays a small line indicator representing the current map scale
Scale display: Displays the current map scale
Scale selector: Displays and changes a map scale
Search router: Enables a configurable search via SQL
Share URL: Shares the current map view via URL
Simple Search: Enables a configurable search on JSON sources (e.g. Solr)
Sketches: Enables a drawing tool with different shapes
View manager: Saves map states for later restoration
WMS loader: Loads a WMS via a getCapabilities-Request
Try it yourself¶
add a Map Element to the content of your application
add a Layertree to the content of your application
add a button that opens the Layertree to the top of your application
add the Navigation Toolbar to the content
add a Copyright and change the copyright text
add an SRS Selector to the footer
4. Configure Sources¶
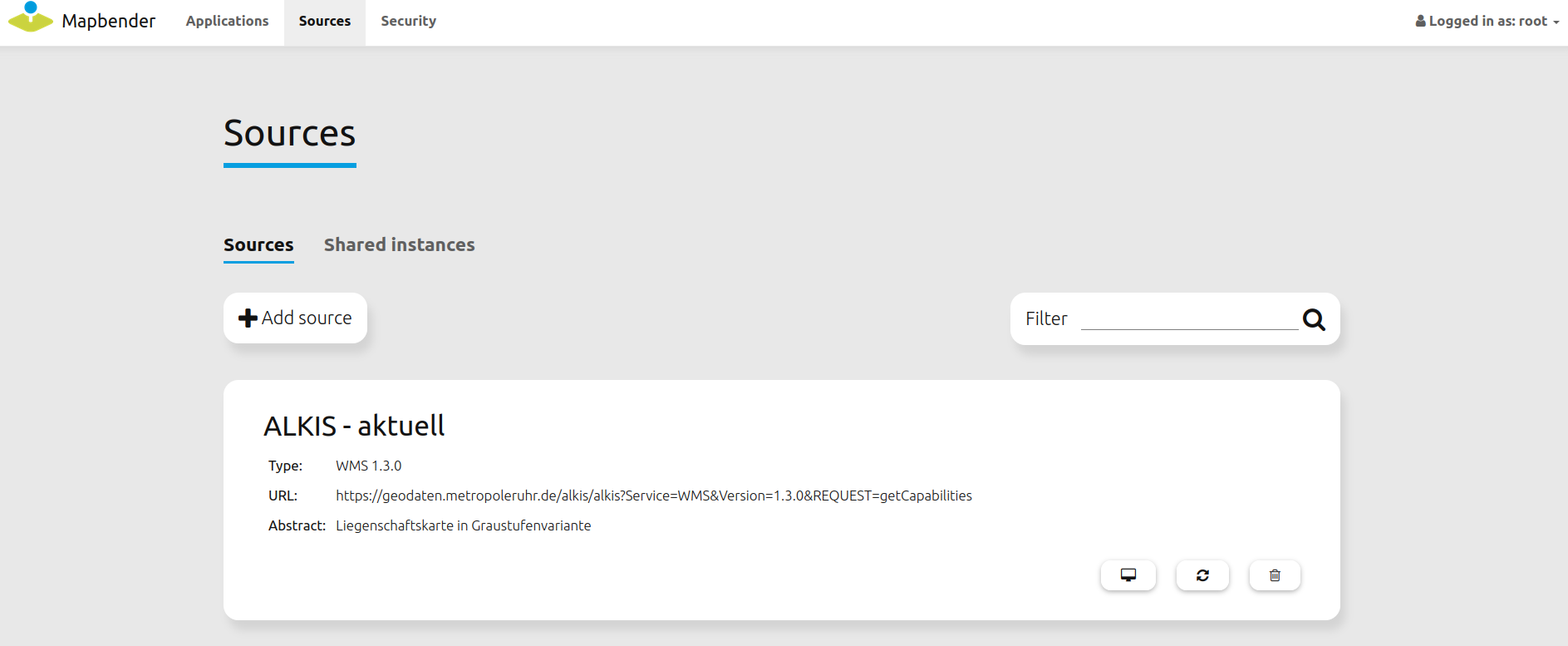
Mapbender can handle sources of the type OGC WMS or OGC WMTS / TMS. Via a click on Sources, one can navigate to an overview of all uploaded sources. There is a second list called “Shared instances” which only provides sources of the type shared. Further information about bound and shared instances can be found here: _layerset:.
The sources pages provides a user with the following functions:
Load sources¶
Mapbender allows the integration of OGC Web Map Services (WMS) and Web Map Tile Services (WMTS). The versions 1.0.0 and 1.3.0. are supported. A source provides a XML, when the getCapabilities document is requested. This information is read by Mapbender. The client receives all necessary information about a source via this XML.
Tip
You should check your capabilties document in your browser before uploading the service.
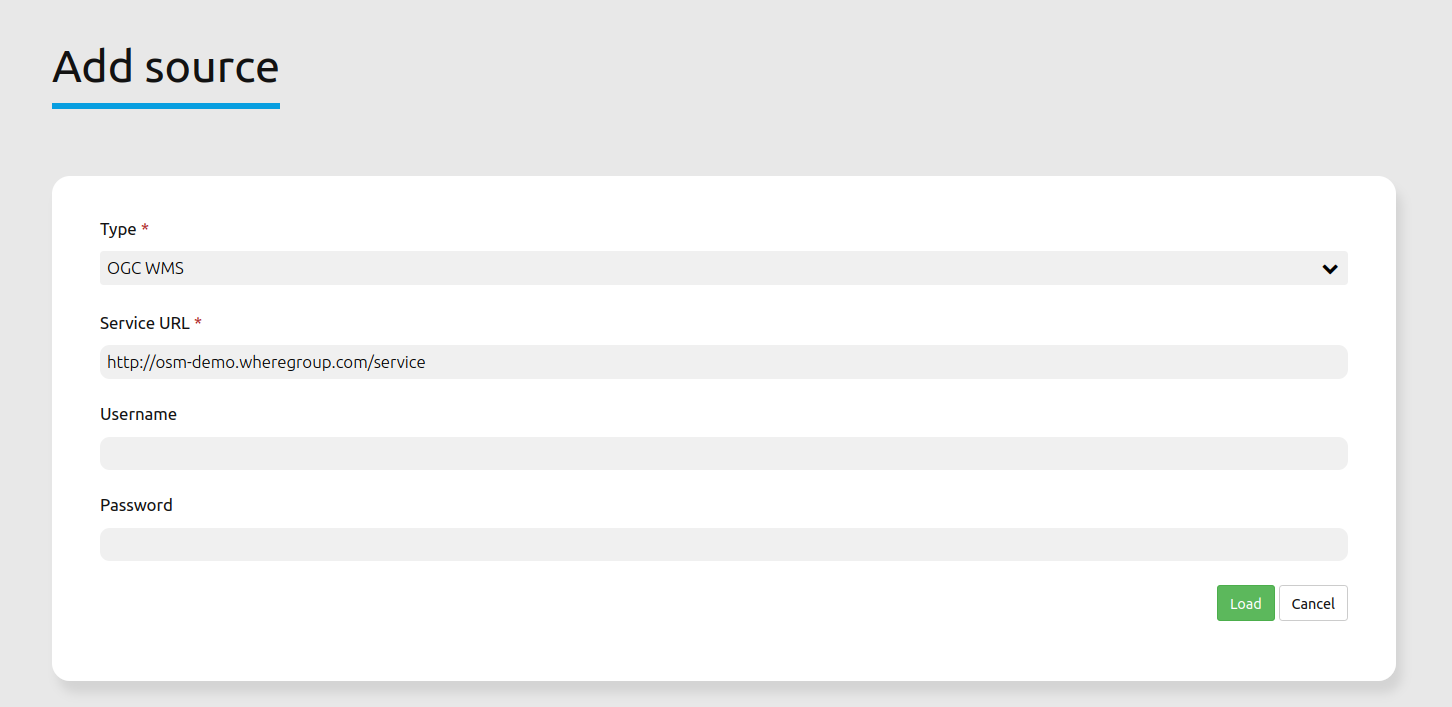
To upload a source, click on
Add source.Define the “Type” of the source: OGC WMS oder OGC WMTS / TMS.
Provide the link to the getCapabilities URL in the field “Service-URL”.
Define username and password in case your source requires it.
Click on “load” to upload the service in the repository.
After a successful upload, Mapbender will provide an overview of the WMS information.
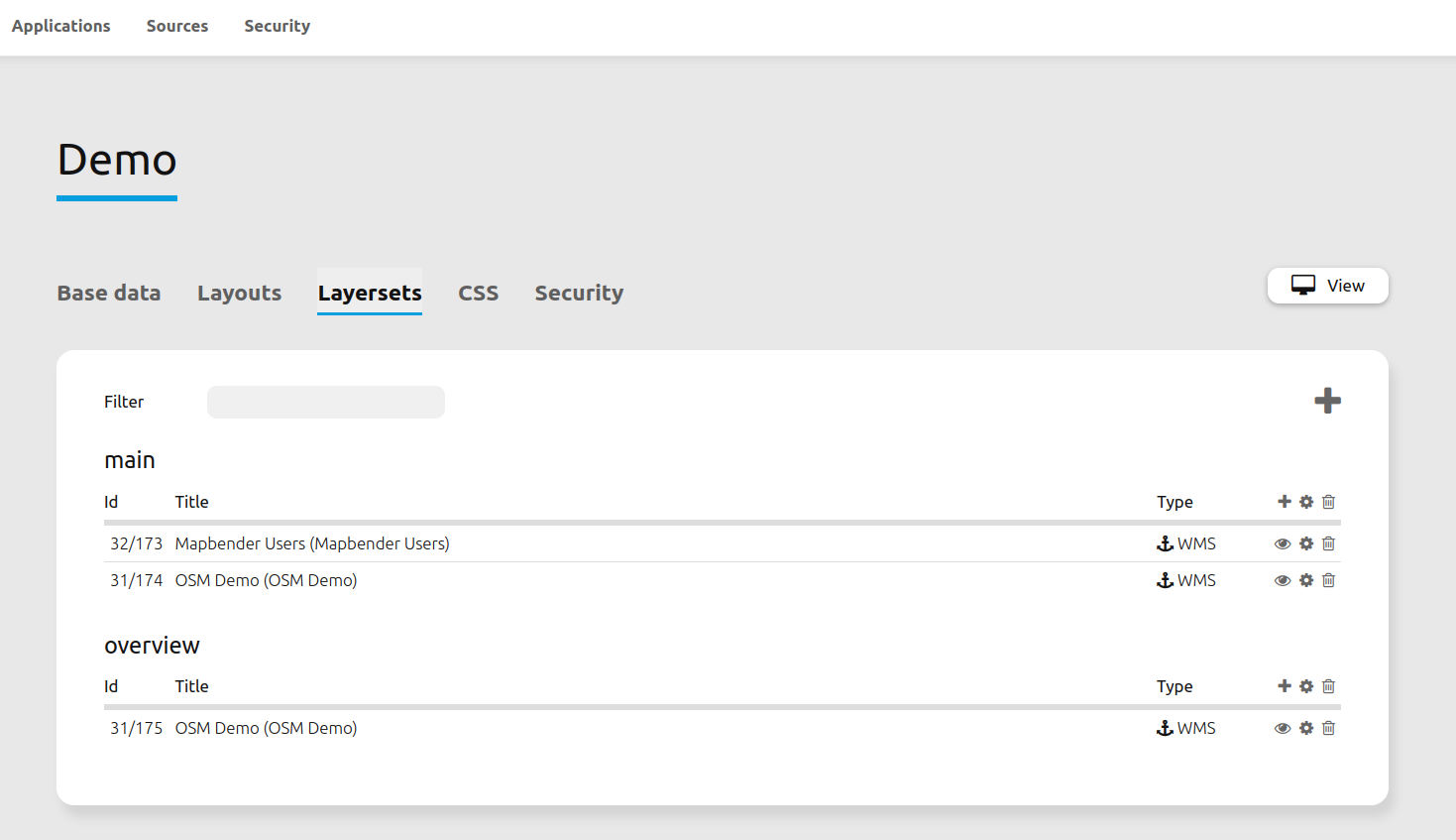
Add sources to an application¶
After uploading a service, it can be integrated into one or several application(s).
Navigate to your application overview page. Click on the

Buttonof the desired application and navigate to the tab Layersets.In the section layersets you can integrate uploaded sources into your application. Click on

Buttonnext to the filter function to create a layerset. All layers have to be assigned to one layerset. Provide a name for it (e.g. “main” for the main map and “overview” for the overview map).Now you can add layers to the layerset. Click on the

Buttonnext to the desired layerset.The order of the layers can be changed via drag & drop.
Source configuration¶
Sources can be individually configured. This can be useful if you, for instance, don’t want to display all layers, change the order or titles of the layers, prevent a layer’s feature info output or adjust the scale in which the layers are visible.
Click on
Application -->
Button --> Layersets -->
Edit instanceto configurate an instance.You can now change the instance configuration.
The order of the layers can also be changed via drag & drop.
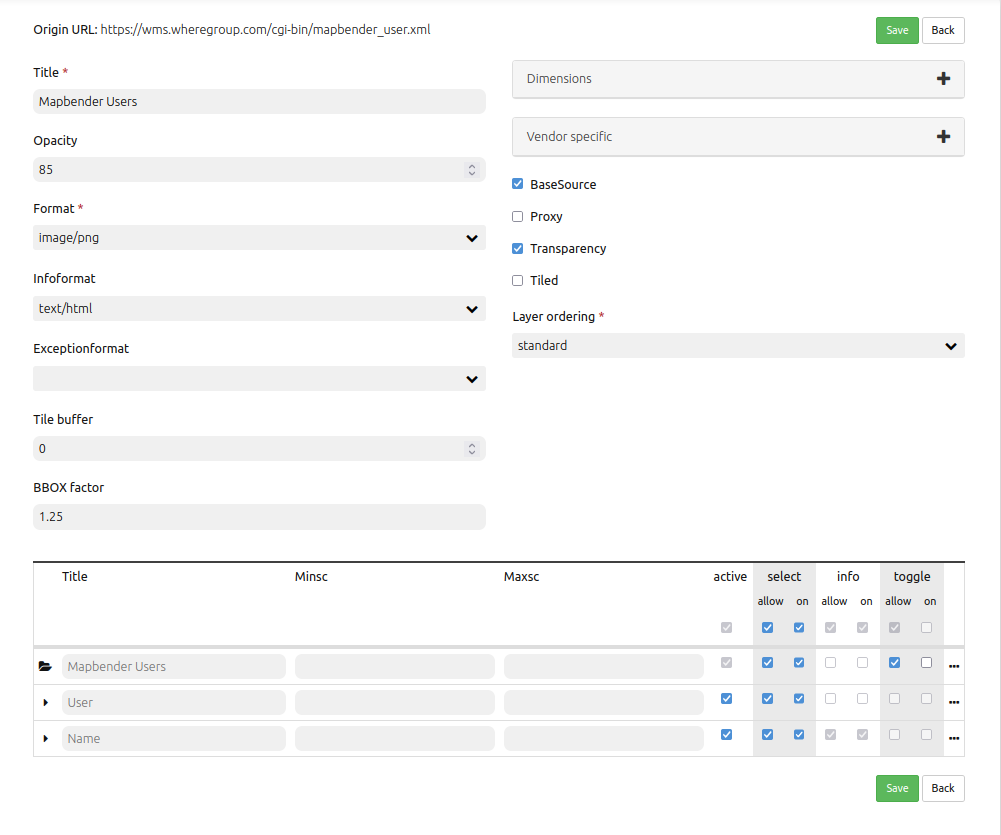
Source configuration:
Title: Name of the application
Opacity: Opacity in percentage
Format: Format of the getMap-Requests
Infoformat: Format of the getFeatureInfo-Requests (text/html für die Ausgabe als HTML wird empfohlen)
Exceptionformat: Format for error messages
Tile buffer: This parameter is valid for tiles services and specifies if additional tiles should be requested. If the user pans the map, these tiles are already downloaded and visible. The higher the value the more tiles are requested (Default: 0).
BBOX Factor: This parameter is valid for non-tiled WMS services. You can specify the size of the returned map-image. A value greater than 1 will request a bigger map-image. Default: 1.25
BaseSource: Should the service be handled as BaseSource (BaseSources can be shown/hidden in the layertree)
Proxy: If active, the service will be requested by Mapbender and not directly
Transparency: default is active, the source is without a transparent background if it is deactivated (getMap-Request with Transparent=FALSE)
Tiled: you can request a WMS in tiles, default is not tiled (may be a good choice if your map is very big and the WMS service does not support the width/height)
Layer ordering: Handles the order of the layers in the service. Can be set to Standard (reversed) and QGIS (same order).
Dimensions:
This function is relevant for sources with a time dimension. Further information can be found on the following page: Dimensions Handler.
Vendor Specific Parameter:
You can define Vendor Specific Parameters in a layerset instance to add them to a WMS request. This principle follows Multi-Dimensions in the WMS specification.
You can use Vendor Specific Parameters in Mapbender for example to add the user- and group information of the logged-in user to a WMS request. You can also add hard coded values.
The following example shows the definition of the parameter “group”, which transfers the group-value of the logged-in user.
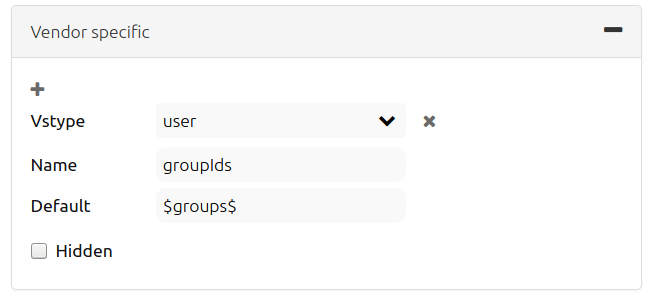
Vstype: Mapbender specific variables. Group (groups), User (users), Simple
Name: Parameter name of the WMS request
Default: Default value
Hidden: If this value is set, requests are send via a server so that the parameters are not directly visible
Currently, the element can be used to transfer user- and group information, e.g. for a user the $id$ and for groups the value $group$.
Layer configuration:
title: layer title
min./max. scale: scale scope
active on/off: activates/deactivates a layer completely
select allow: layer is active when the application starts
select on: selectable in geodata explorer
info allow: layer info is active when the application starts
info on: layer provides feature info requests, info default activates the feature info functionality
toggle allowed: allows opening of folder at application start
toggle on: open folder on start of the application
layer ordering: allows to order layer according to the standard or QGIS configuration.
more information (…): opens a dialog with detailed layer information:
ID: ID of the layer
Name: layer name of the service information (for getMap-Requests)
Style: if a WMS provides more than one style you can choose a different style than the default style.
Try it yourself¶
Load a source into Mapbender.
Add a source to your application.
Change the configuration of your source.
Here is an example source:
5. User and group management¶
Access to Mapbender requires authentication. Only public applications can be used by everyone.
A user can get permissions to access one or a set of applications and services.
Create a user¶
To create a user, go to
Security --> Users --> Add new user.Choose a name for your user.
Provide an email address for the user.
Choose a password for your user and repeat it in the
Confirm passwordfield.Save your new user. It is still possible to alter user information later on.
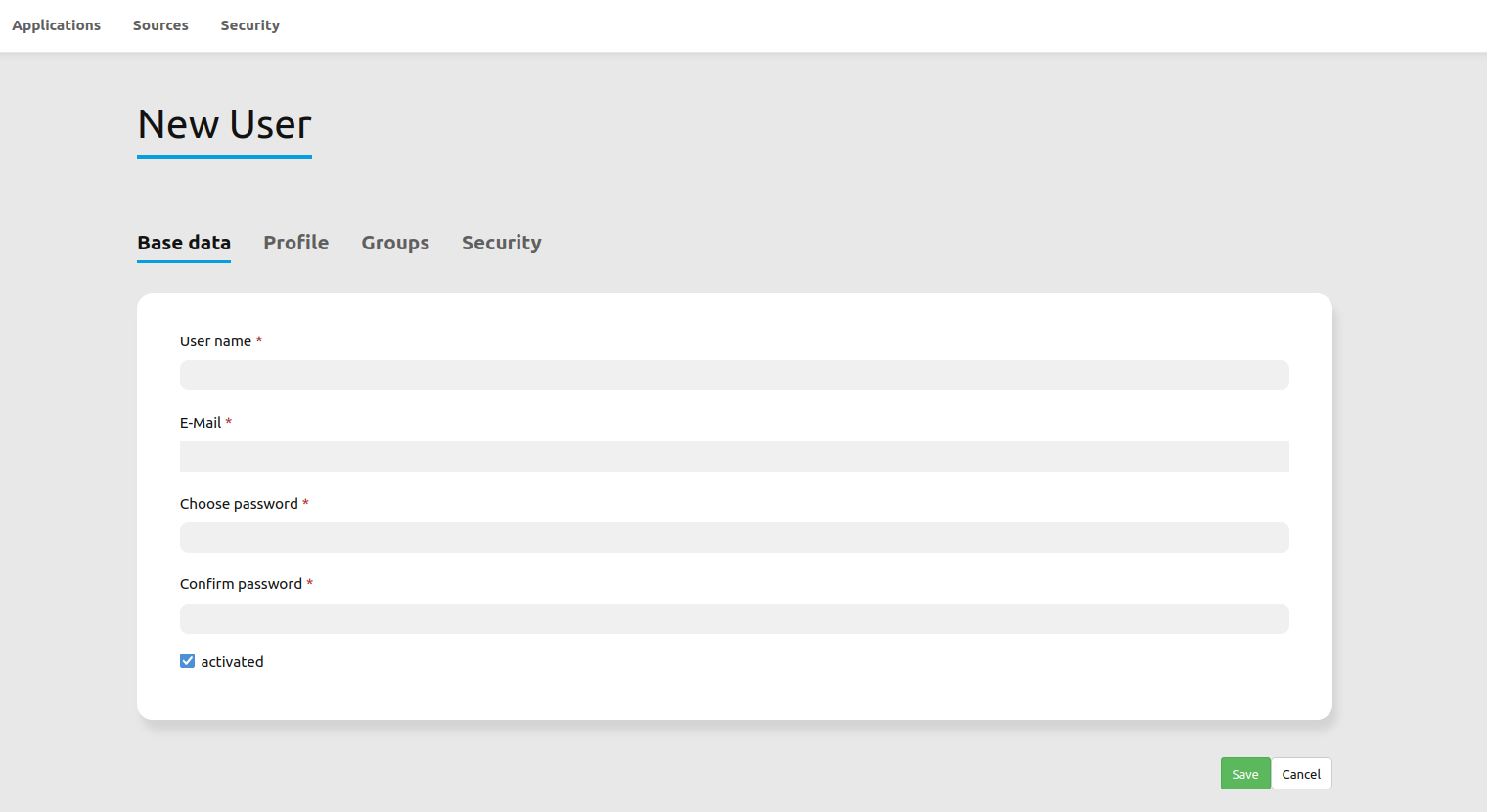
You can provide more information about the user in the tab Profile. In the Groups and Security tabs it is possible to assign the user additional parameters, e.g. the membership to a group.
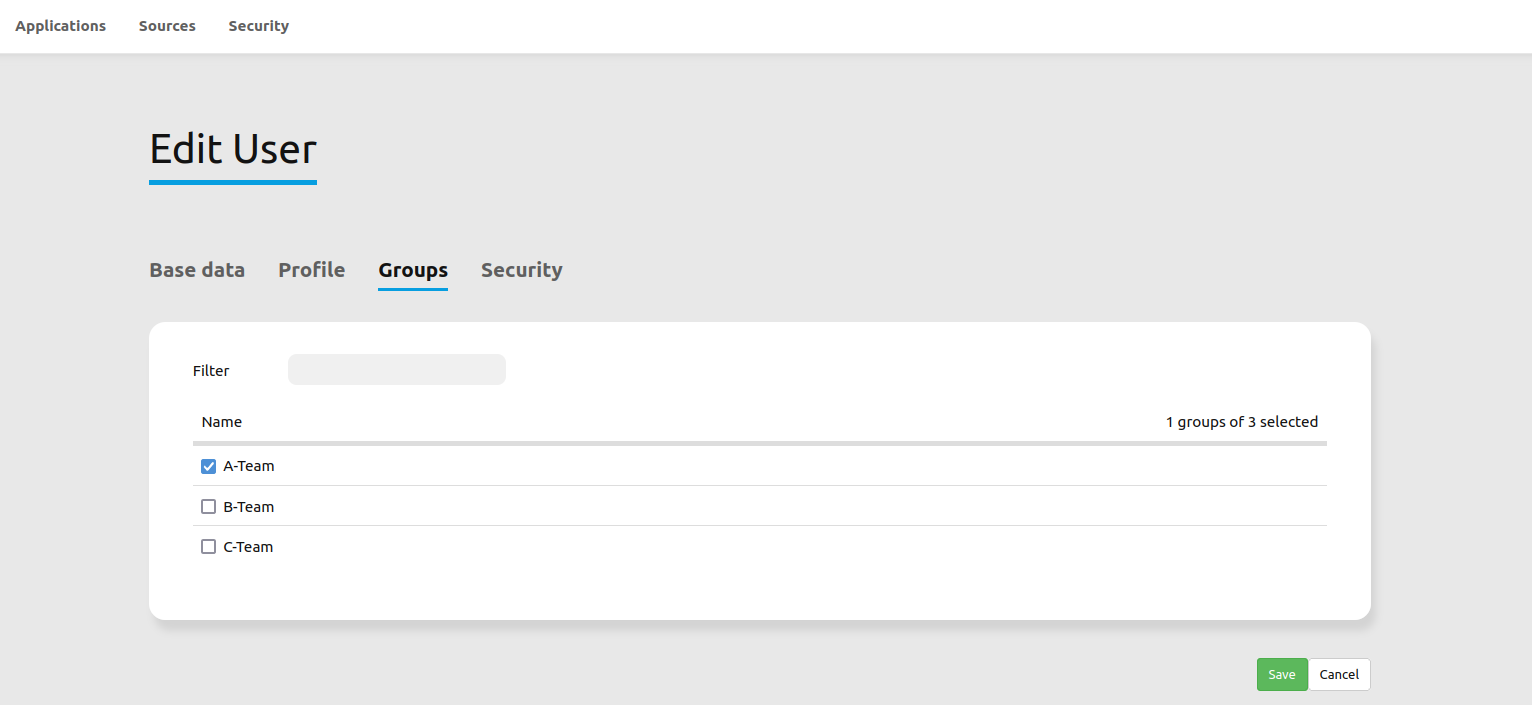
Create a group¶
Create a group by
Security --> Groups --> Add new Group.Define a name and a description for your group.
In the tab
Users, assign users to your group.Save your new group.
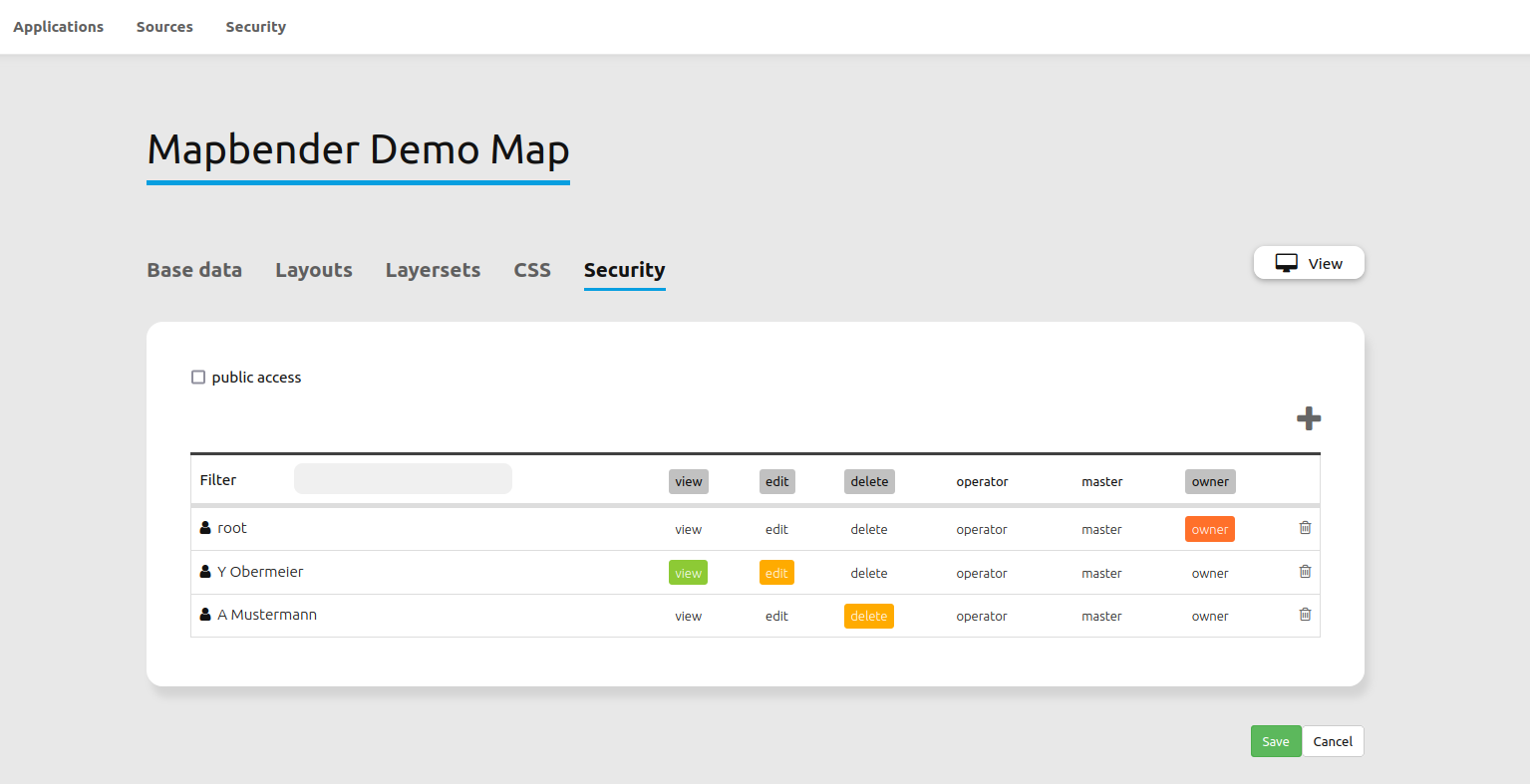
6. Rights management¶
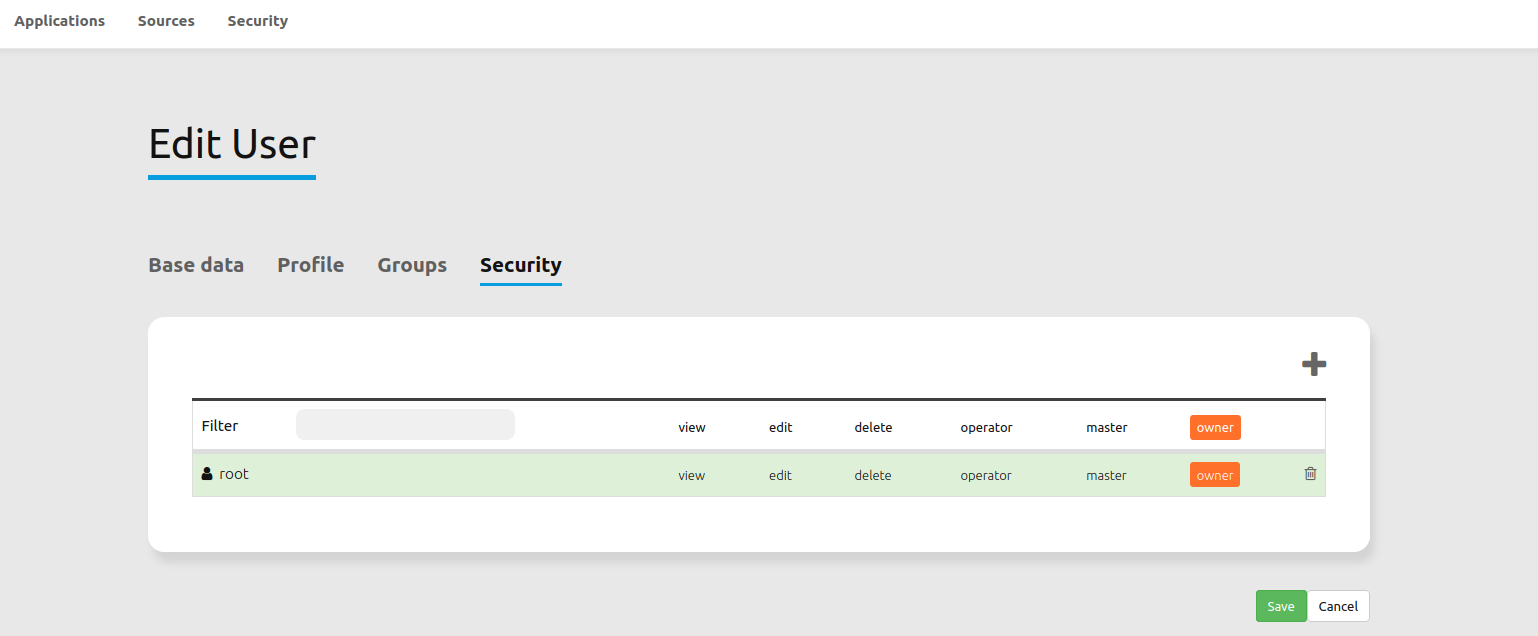
Mapbender provides different rights. They refer to the Symfony ACL System.
view: Whether someone is allowed to view the object.
edit: Whether someone is allowed to make changes to the object.
delete: Whether someone is allowed to delete the object.
operator: Whether someone is allowed to perform all of the above actions.
master: Whether someone is allowed to perform all of the above actions and in addition is allowed to grant any of the above permissions to others.
owner: Whether someone owns the object. An owner can perform any of the above actions and grant master and owner permissions.
Assign roles to a user by Security --> Users --> Edit your User --> Security.
Assign an Application to a User/Group¶
Edit your application via
Application --> `` |mapbender-button-edit| ``Edit-Button.Choose
SecurityPublish your application by
Security --> public access. Alternatively, one can use the
Button. If this option is activated, also anonymous users will gain access to the application.Set permissions for specific users/groups.
Test your configuration. Logout from Mapbender by Logout. Login again as the new user.
Assign elements to a User/Group¶
Per default, all elements are accessible to users/groups if they have access to that particular application. This can be modified for each element.
Edit your application by
Application --> `` |mapbender-button-edit| ``Button.Choose
LayoutsEvery element has a

Acl-Button.Choose the

Acl-buttonfrom the element that should be only available for special users/groups.Assign one or more users or groups to the element. Then, set permissions like view, edit, delete, operator, master, owner
Test your configuration.
7. Start Application at a defined position¶
You can open an application at a defined location. This can be done by a POI. You also can add texts in the request.
You can pass one or more POIs in the URL. Each POI has the following parameters:
point: coordinate pair with values separated by comma (mandatory)
label: Label to display (optional)
scale: Scale to show POI in (optional, makes only sense with one POI)
If you pass more than one POI, the map will zoom to 150% of the POIs bounding.
To pass a single POI, use the following URL format:
?poi[point]=363374,5621936&poi[label]=Hello World&poi[scale]=5000
What’s next?¶
This is only the first step on the road to using Mapbender. There is a lot more functionality you can try.
Mapbender Website: https://mapbender.org/
You find tutorials at: https://doc.mapbender.org
Get involved in the project: https://mapbender.org/en/community/
 update data source
update data source